I knew Windows Azure SQL Databases have been around for a couple of years but never had the time or need to research them. With a possible data center consolidation in the future, I was wondering if my company could leverage a Windows Azure SQL Databases to reduce the total cost of ownership for certain applications?
Today, I will be working with the sample [AUTOS] cloud database that I created in a previous blog. I want to test connectivity to this cloud database using common programs and tools that my users or developers might choose.
The SQL Server 2012 feature pack download from Microsoft comes with two tools that most database developers know about: BCP and SQLCMD. I will be testing how these tools work with a Azure database.
A command line tool like SQLCMD can be used to issue most, if not all TSQL commands. It is great for ad-hoc queries with small result sets.
This includes Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands to SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE data.
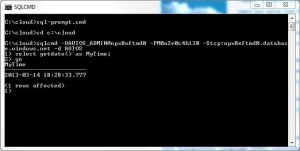
The command file below connects to the [AUTOS] database in the cloud, executes the commands in the input file, and saves any results to the output file. I was able to successfully run the above commands.
dml-run.cmd
dml-input.txt
dml-output.txt
Another good test for SQLCMD is to execute Data Definition Commands to CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, and DROP TABLE.
The command file below connects to the [AUTOS] database in the cloud, executes the commands in the input file, and saves any results to the output file.
ddl-run.cmd
ddl-input.txt
ddl-output.txt
I was able to add a new table named [STAGE].[MAKES] with constraints and keys. I loaded the table with data from the staging scheme and displayed the current state of the table. Last but not least, I removed the table at the end of script.
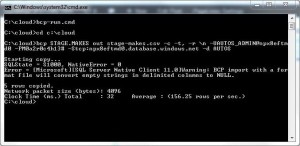
I ran this script one more time to have a table to use in my BCP example. A cool thing out BCP is that it can be used to load or dump data.
The example below has a command file that dumps the contents of the [STAGE].[MAKES] to a local Comma Separated Values (CSV) file.
In a nutshell, the command line utilities that can be downloaded as part of the feature pack work fine with an Azure SQL database. Just make sure you have the user name, password, and connection information entered in correctly. These utilities use the SQL Native driver to talk to the cloud.
Next time, we will explore what can be done with MS Access using an ODBC connection to talk to our Azure SQL database.